The Reward-Sharing Scheme (RSS) on Cardano is a mechanism designed to distribute rewards earned from staking and block production among stake pool operators (SPOs) and delegators who delegate their ADA to stake pools. This system incentivizes both stake pool operators and ADA holders to participate in securing the network through staking while ensuring that rewards are fairly shared based on each participant’s contribution.
Key Elements of the Reward-Sharing Scheme (RSS)
- Stake Pool Operators (SPOs):
- Stake pool operators are responsible for running the infrastructure needed to produce blocks and validate transactions on the network. When a stake pool is selected to produce a block (based on the amount of ADA delegated to it), it earns rewards for doing so.
- SPOs are compensated for their work and expenses through the rewards-sharing mechanism, which allows them to take a portion of the rewards.
- Delegators (ADA Holders):
- ADA holders can delegate their ADA to a stake pool without transferring ownership of their ADA. When the stake pool they’ve delegated to earns rewards, the delegators receive a share of those rewards based on the amount of ADA they’ve staked.
- Delegators are not responsible for running a node but contribute to the network’s decentralization by supporting the stake pool.
- Reward Distribution:
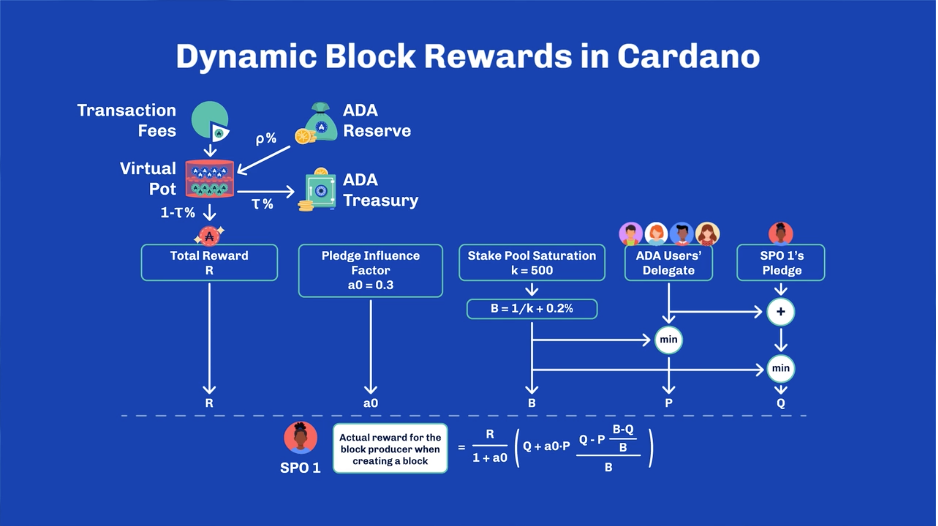
- The total rewards a pool earns in an epoch (5-day period) are divided between the stake pool operator and the delegators.
- The reward-sharing formula ensures that SPOs are compensated for their work (fixed costs and a portion of the rewards), and delegators earn rewards proportionate to their stake in the pool.
- Key Components of the Reward Formula:
- Fixed Cost: A fixed fee is taken by the SPO to cover the operational costs of running the stake pool, such as maintaining the hardware and infrastructure. This is subtracted from the total rewards before distribution to delegators.
- Margin: SPOs can set a margin, which is a percentage of the remaining rewards (after the fixed cost) that the operator keeps as profit. The margin incentivizes SPOs to run high-performing pools.
- Delegator Rewards: The remaining rewards, after the fixed fee and the margin, are distributed to the delegators in proportion to the amount of ADA they have staked in the pool.
- Pool Saturation:
- The reward-sharing scheme also takes into account pool saturation. If a pool has more ADA delegated to it than the optimal level (determined by the k-parameter), the rewards for that pool start to decrease, encouraging ADA holders to delegate to smaller, under-delegated pools. This helps maintain decentralization by preventing large pools from dominating the network.
- Incentives for Decentralization:
- The reward-sharing scheme is designed to incentivize decentralization by encouraging the creation and delegation to smaller pools, preventing a few pools from controlling too much of the network’s total stake. Delegators are rewarded more when they stake to well-performing, decentralized pools.
Example of Reward-Sharing
Assume a stake pool produces a block and earns 1000 ADA in rewards during an epoch.
- Fixed Cost: The stake pool operator has set a fixed cost of 340 ADA to cover operational expenses.
- Margin: The SPO has set a margin of 2%, meaning they will take 2% of the remaining rewards (660 ADA) after the fixed cost is subtracted.The operator takes 13.2 ADA (2% of 660 ADA) as a margin, leaving 646.8 ADA to be distributed to the delegators.
- Delegator Rewards: The remaining 646.8 ADA is distributed proportionally to the delegators based on the amount of ADA they have staked in the pool.
Importance of the Reward-Sharing Scheme
- Fair Compensation: The RSS ensures that both stake pool operators and delegators are fairly compensated for their roles in maintaining and securing the Cardano network.
- Network Security: By incentivizing staking and block production, the RSS plays a key role in the security and sustainability of the Proof-of-Stake system, ensuring that a large number of stakeholders are participating in the consensus mechanism.
- Decentralization: The RSS, combined with the saturation parameter, encourages decentralization by pushing delegators toward smaller pools and preventing the centralization of stake in just a few pools.
- Transparency: The RSS provides transparent and predictable reward distribution, allowing delegators to choose pools based on factors such as the fixed cost, margin, and performance history of the stake pool.
Conclusion
The Reward-Sharing Scheme (RSS) on Cardano is a well-structured mechanism that ensures the fair and transparent distribution of staking rewards between stake pool operators and delegators. It incentivizes both parties to participate in the network, promoting decentralization, security, and sustainability. By allowing ADA holders to passively earn rewards through delegation, the RSS also ensures that the network can scale securely while maintaining a high level of decentralization.

Leave a Reply