Sharding is a concept in blockchain technology designed to improve scalability by breaking the network into smaller, more manageable parts (shards) that can process transactions in parallel, thus reducing the load on any single node and increasing the network’s overall throughput.
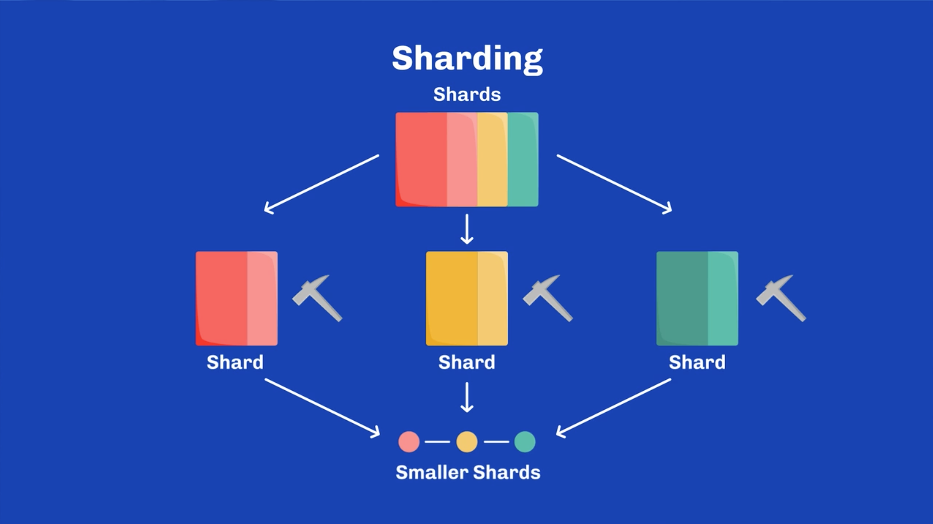
However, Cardano does not currently implement sharding in the traditional sense that some other blockchains like Ethereum are exploring.
Instead, Cardano uses a different approach to achieve scalability. The network leverages a layered architecture and advanced protocols like Ouroboros Hydra and Ouroboros Praos to achieve efficient scaling without the need for sharding.
- Ouroboros Hydra: This is a scaling solution built on top of Cardano that allows for off-chain processing of transactions through Hydra Heads. Each head operates as a mini-blockchain that can process transactions independently and in parallel with others, significantly boosting throughput while still maintaining security and decentralization. This approach shares some conceptual goals with sharding but doesn’t divide the main blockchain itself.
- Layered Design: Cardano separates the settlement layer (where ADA transactions occur) from the computation layer (where smart contracts are executed). This layered design is meant to optimize scalability without fragmenting the network, like in traditional sharding.
While sharding may be a popular scalability solution in other blockchain ecosystems, Cardano’s unique design and the development of solutions like Hydra aim to achieve similar results—scalability, speed, and decentralization—without traditional sharding.


Leave a Reply